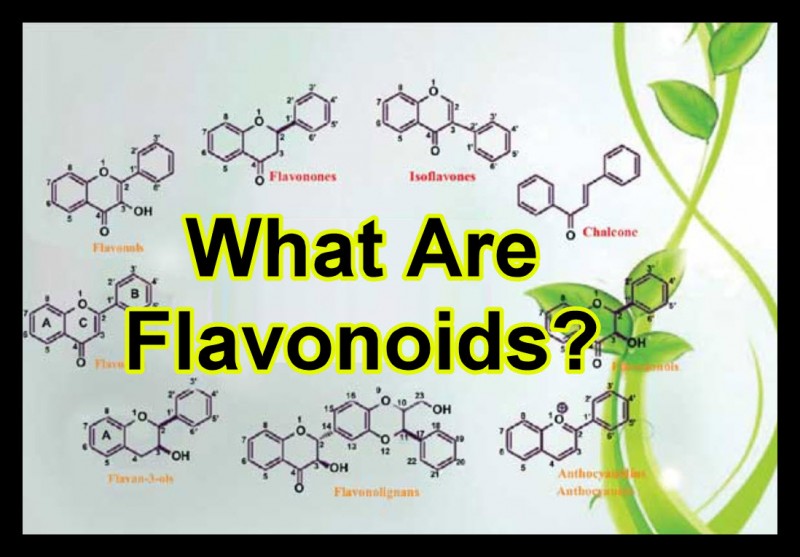
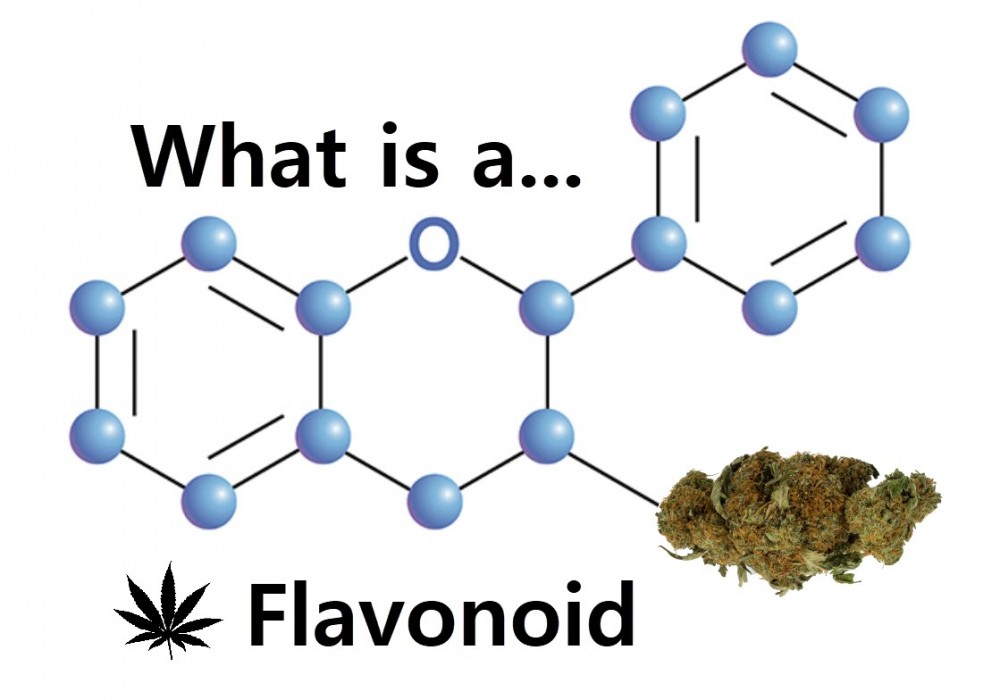
What Are Flavonoids?

Cannabis contains many important compounds. THC (tetrahydrocannabidiol), which is responsible for your high, as well as CBD (cannabidiol), are two of the most well-known compounds in cannabis but there are many more that are equally fascinating.
One of these are flavonoids, which aren’t unique to cannabis. Flavonoids are responsible for the non-green colors you see in other plants – the yellow in sunflowers, the red in raspberries. In cannabis, flavonoids are what give certain strains its color. Together with other cannabinoids as well as terpenes, flavonoids contribute to a wide spectrum of effects, aromas, and flavors. Flavonoids also have health benefits, but also contribute to the smell, taste, and sensory experience involved when you consume a cannabis strain.
Flavonoids in cannabis, known as cannaflavins, are the least understood parts of the cannabis plant due to the federal prohibition. However, we know that there are 4 main groups of flavonoids: flavonoids, neoflavonoids, isoflavonoids, and anthocyanins. But for simplicity, let’s refer to all of them as flavonoids. During the growth phase of the cannabis plant, it also serves important functions in the plant. These include protection from pests and fungi, attracting pollinators, and function as UV filters. Scientists are already very familiar with the flavonoids that exist in other (legal) plants that we use or consume everyday, especially those found in fruits and vegetables. They have identified over 6,000 flavonoids that exist in the world today, yet only around 20 cannaflavins are known to man.
Most flavonoids have powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Some examples of cannaflavins and their health benefits include:
Catechins: Also found in tea, cocoa, and some fruits, catechins are known to promote heart health. Catechins have anti-hypertensive, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties and helps ensure that cholesterol levels are healthy.
Vitexin and Isovitexin: Both cannaflavins have demonstrated anti-cancer properties. Studies show that both cannaflavins have chemoprotective properties and fight cancer by encouraging the death of cancer cells.
Epigenin: Studies show that epigenin is beneficial in preventing cancerous tumors. Epigenin also has anti-inflammatory properties, and aids in the death of cancer cells.
Orientin: Orientin is one of the most popular flavonoids in the plant community, with numerous health benefits. One study showed that orientin alone has anti-aging, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, and painkilling properties. It also noted that orientan works as a vasodilator and helps support heart and brain health.
Quercetin: Quercetin is found in numerous fruits and vegetables. It is known for its antioxidant properties; it’s also effective in fighting viruses. Studies show that quercetin has been beneficial in inhibiting the influenza virus.
Cannaflavin-A: A powerful anti-inflammatory agent, it is said that cannaflavin-A is more effective than aspirin. Cannaflavin-A works like an NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) that inhibits the PGE-2, a prostaglandin that stimulates the inflammatory response in the body.
Silymarin: Thyme has the highest concentration of silymarin, a flavonoid with numerous health benefits. Its therapeutic properties have been known since ancient Greece, particularly for its benefits for treating liver problems.
Luteolin: Found in clover and ambrosia as well, luteolin has been shown to be beneficial in treating infections and treating cancerous tumors.
Kaempferol: Known for its anti-depressant and cancer-fighting properties, kaempferol can help reduce the risk of cancer and certain heart ailments.
Apigenin: Also present in chamomile, celery, and parsley, apigenin has anti-inflammatory and anti-anxiety properties.
Beta-sitosterol: A cannaflavin that is also present in avocadoes and nuts, beta-sitosterol has documented anti-inflammatory properties.
The flavonoid levels in cannabis can make up as much as 2.5% of its dry weight, although it’s likely not found in the seeds and roots. Flavonoids work with other compounds in the cannabis plant for the “entourage effect”, which is the reason why whole plant medicine is always better than isolated compounds. In short, when the hundreds, or even thousands, of compounds in the cannabis plant are taken together, they enhance each other health benefits. Whether it’s terpenes, terpenoids, flavonoids, or cannabinoids, using whole plant medicine offers more powerful therapeutic properties because of the entourage effect.
Studying flavonoids is still very much in its early stages, but only when federal restrictions on cannabis are lifted will we be empowered with much more knowledge on flavonoids as well as the other valuable components in the cannabis plant.
OTHER STORIES YOU MAY ENJOY...
WHAT ARE WEED FLAVONOIDS EXACTLY, CLICK HERE.
OR..
WHAT ARE TERPENES AND WHY ARE THE BIG, CLICK HERE.
OR..
WHAT ARE TERPENES, CLICK HERE...
OR..