Could Glycine Receptors be the Pathway for Cannabinoids to Relieve Pain?
Glycine receptors (GLyRs) have been discovered in the mid- ‘50s by scientists, but they had a hard time identifying therapeutic agents targeting these receptors. In the process of finding therapeutic ways to treat specific chronic pain and pain-related disorders, they stumbled on the probability that glycine receptors could be involved in pain relief. It is already an accepted fact that cannabis is used to treat pain. Now they identify the specific effect of cannabis-mediated glycine receptors too.
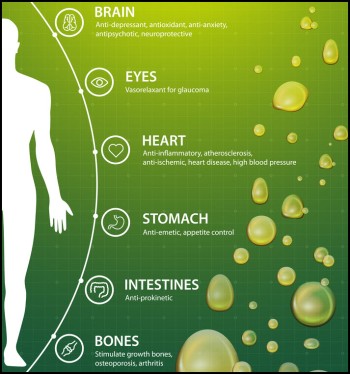
Opioid-based drugs were until very recently the go-to drug to manage pain, but not everyone responds positively to the effect of these drugs. In fact, a survey found that only about 58% of patients taking opioid-related painkillers, were relieved from their pain. Opioids can be very hard on the body and have many side-effects. These side-effects include constipation, vomiting, respiratory depression, and addiction. Sometimes it can be fatal. For this reason, safer alternatives are looked into and cannabis is high on the list of drugs with positive outcomes.
In studies, it has been found that GLyRs are a primary target for exogenous and endogenous cannabinoids in the central nervous system. Cannabinoids augment the function of glycine receptors in a variety of neurons in the brain. But because too little was known about the molecular mechanism and behavioral implication of cannabinoid modulation of GLyRs, it was mostly ignored. In recent research, molecular insights into cannabinoid-GLyR interaction have been explored. There is more clarity on the molecular basis of the cannabinoid modulation of GLyRs.
How does Pain Pathway Work?
Pain gets regulated in the central nervous system by using specialized cells called neurons. There is communication between the cells through chemical and electrical events. This is called an action potential. When this happens, the neurotransmitters release and stimulate the next neuron in the pathway. This neuron is called the postsynaptic neuron.
Depending on what neurotransmitter is released, the binding will either have an excitatory or inhibitory effect. An excitatory effect will make the neuron more positive because there was an influx of positively charged calcium ions. An inhibitory effect has the exact opposite result. It becomes negative because there was an influx of negatively charged chloride ions.
When the neurons are overexcited, it continuously stimulates the pain pathway through the spinal cord until it finally reaches the brain. Cannabis manipulates the flow of calcium and chloride ions. By doing this, cannabis effectively dulls the over-excited neurons to control pain.
What are Glycine Receptors Exactly?
Glycine receptors belong to the Cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel (LGIC) family. It is a group of membrane ion channel receptors. It is critical for fast synaptic neurotransmission in the central nervous system. Glycine Receptors act as primary inhibitory receptors in the spinal cord. They open channels allowing an influx of chloride into the neuron and inhibit the neuron to reach an action potential. For the glycine receptors to be activated to open the chloride channel, three glycine molecules need to bind to the receptor. Other molecules can also augment the activity of glycine receptors. CBD forms part of these molecules.
The Therapeutic Benefits of Cannabidiol
Some studies prove that CBD is very effective in the reduction of inflammation and neuropathic pain without the occurrence of analgesic tolerance. Analgesic tolerance means the patient needs and increase of the drugs to relieve pain. This makes it important to find something that avoids analgesic tolerance because the higher a dose, the more damaging side-effects occur. Because CBD is able to keep stable doses during treatment, it makes it a very positive treatment to manage chronic pain. Further research indicates that CBD is involved in the pain pathway. CBD targets the glycine receptors in the spinal cord causing the expected inhibitory effects in the pain pathway to the brain.
Similar results were found with the effect of THC and CBD on the calcium channels. Instead of opening the calcium ion channel, the binding of THC and CBD provokes the channel to close. Positively charged ions are stopped from entering the neurons and action potential is not reached. In animal testing, great success is achieved. What needs to happen now, is clinical testing in humans.
Therapeutic potential of glycinergic cannabinoids.
Suppression of acute and chronic pain
Cannabis relief chronic pain as some of the THC-induced cellular and behavioral effects are independent of CB1 receptors
Relieve neuropathic pain
THC can lower pain intensity in patients that suffer from chronic neuropathic pain. A THC/CBD spray also suppresses peripheral neuropathic pain. Even with patients that are resistant to other treatments. THC/CBD proved a significant improvement in pain management and sleep.
Conclusion
Understanding the cannabinoid-GLyRs interaction, allow scientists to study a whole new way to separate cannabis-induced analgesic effects from cannabis-induced psychoactive effects. GLyRs should emerge as therapeutic targets for non-psychoactive cannabinoids in the treatment of many neurological diseases with a GLyR deficiency.
CANNABIS PAIN RELIEF, YOU BET, READ MORE...
PAIN RELIEF TRY HIGH THC FLOWER, CLICK HERE.