Graphical Guide to the Most Abundant Terpenes in Cannabis

Perhaps you’ve already pondered what gives each specific strain its flavor and fragrance, and the answer lies within the terpenes, which are the molecules “in charge” of the overall aroma of a strain.
All cannabis varieties have a common dominant fragrance that so many enthusiasts find pleasurable, but the exact amount of terpenes found in a strain will determine its exact smell and taste.
Scientists have figured out that there are around 120 different terpenes in cannabis, and about 80-100 can only be found within the marijuana plant.
Some terpenes are frequent in many strains, but are also present in many other plants.
Because there are so many different terpenes, the aroma and the fragrance of each strain can differ greatly. They can resemble the scent and flavor of citrus fruits, lavender, mint, pine, musk, various berry-fruits and some can have strong musky earth-like odors.
What’s also very important about these molecules is that they have a far more beneficial role beside only providing the cannabis plant its scents and flavors. They actually play a very important medicinal function, as they “collaborate” with the cannabinoids THC and CBD, to create the full effect cannabis is renowned for.
Just like cannabinoids, terpenes originate in the flowers of the female plants, inside the tiny mushroom-like resin glands called the trichomes.
Besides being found in plants, these natural molecules are also present in some species of the animal kingdom, like certain kinds of butterflies and termites.
There is one more group of compounds under the “terpenes” umbrella and these are terpenoids, which have additional functional groups, but after the process of decarboxylation terpenoids lose these groups, and become terpenes. The same chemical process turns the tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) into the regular cannabinoid THC.
When we look at terpenes from a strictly chemical standpoint, they consist of the replicated organic molecule isoprene. The function of terpenes within the plant itself is to deter various pests and predators from attacking the plant, while the second function is that they collaborate with cannabinoids to create resin in the buds.
Terpenes found in other plants have been used for the production of fragrances, essential oils and beauty products for centuries. They’ve also found their use in traditional and alternative medicine, and they play a capital role in aromatherapy.
Besides being abundant in nature, synthetic terpenes are also created in labs for various uses.
But let’s get back to marijuana. As I previously mentioned, these aromatic compounds play a paramount role, besides being responsible for a rainbow of tastes and odors.
The Relationship of Terpenes and Cannabinoids
When we ingest the flowers of the cannabis plant, we consume both the cannabinoids (THC, CBD, etc), and terpenes at the same time.
While the terpenes aren’t psychoactive like THC, they provide the user with additional health benefits and help shape the type of “high”. When this happens, terpenes and cannabinoids play off each other in what’s called the “entourage effect”. We’ll touch upon this in more detail soon enough, but now you should check out what are the functions of the most prominent terpenes in cannabis.
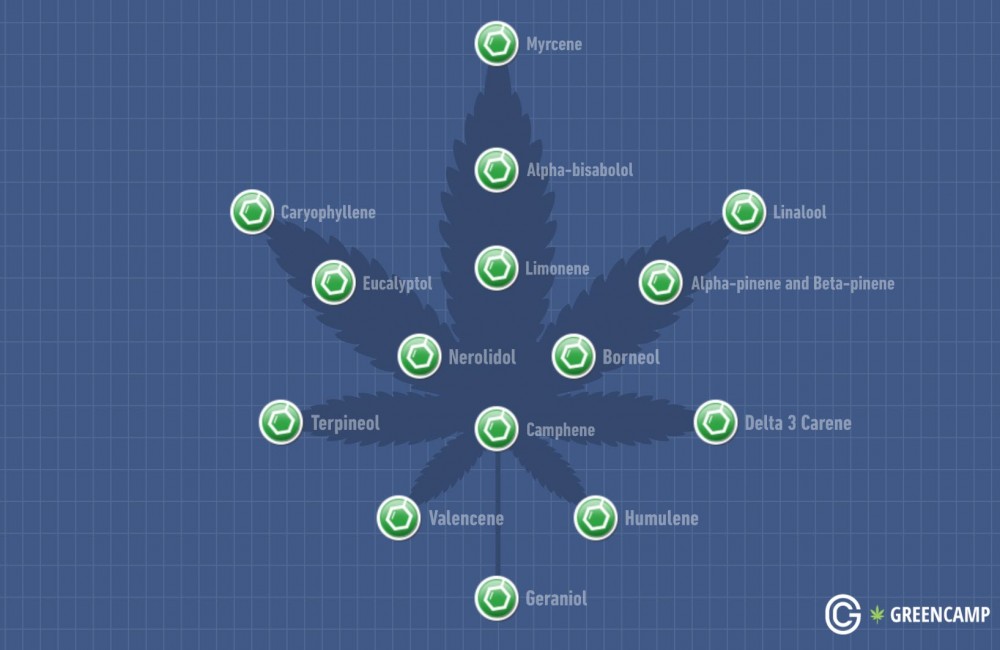
The term “entourage effect” was first coined by Israeli scientists Raphael Mechoulam (who also discovered THC) and S. Ben-Shabat in 1998, and it entails how exactly cannabinoids and terpenes cooperate within our bodies (via the endocannabinoid system), to maximize the beneficial medical effects of cannabis as a whole.
This means that if we were to ingest only a specific cannabinoid that was separated from the plant using laboratory equipment, the overall health-effects would significantly diminish, because of the lacking of terpenes (and other cannabinoids).
Because of this, it’s ideal to use entire cannabis flowers as a treatment method (no matter if it’s smoking, vaping, or any other kind of ingestion), as this allows the full potential of the plant to be unleashed.
This point is also frequently made by Martin A. Lee, who is one of the world's leading experts on cannabidiol (CBD).
As you can see in the graphic above (with additional details about each individual terpene), the interaction of terpenes on cannabinoids is responsible for many different effects, ranging from a better absorption of cannabinoids by the endocannabinoid system (by increasing cell permeability), aiding with fighting bacterial defenses, lessening of the negative aspects of cannabinoids and even accumulating serotonin levels, which works wonders on the general mood of an individual.
Let’s now cover 4 terpenes that are the most abundant in all cannabis varieties. It’s should be noted that these terpenes (even though most plentiful) aren’t present in all cannabis strains.
Myrcene
As the most prominent cannabis terpene, scientists have figured out the myrcene makes around 65% of all terpenes in numerous cannabis strains. Even though it isn’t unique to pot, it is mostly found in this plant. Its scent and taste can be described as a combination of earthy musk-like tones, with a twist of grape/fruity flavors.
It’s useful for the reduction of inflammation and pain sensations, and indica strains are where it’s mostly found in larger quantities.
Beta-Caryophyllene
This terpene has a pungent, spicy and pepper-like aroma, and besides cannabis it’s also present in oregano, basil, rosemary, basil, cloves and black pepper.
What’s very interesting about beta-caryophyllene is that it binds to the CB2 receptors in our endocannabinoid system (just like the cannabinoid THC), which technically makes it a cannabinoid, even though it is a terpene.
It’s quite useful for anxiety, inflammations, pain treatment and this study showed that it even helps with alcohol addiction, as it lowers the voluntary intake of alcohol. This study was conducted on mice, but the same principle can be transferred to us humans, as additional testing will surely prove in the future.
Linalool
This specific terpene is very abundant in other plants besides cannabis, and can be found in cinnamon, lavender, mint and coriander.
All of these plants provide aromatic relief and have relaxational attributes (to a certain extent because of linalool). It’s has a floral and somewhat-spicy fragrance, and is beneficial for a wide range of conditions, such as insomnia, depression, epileptic seizures and arthritis.
Limonene
Also very abundant in a lot of strains, limonene (as the name entails) closely resembles the aroma of lemons and other citrusy fruits, because these fruits also have large amount of this terpene in their structure.
Limonene is quite beneficial for mood improvement and acts as a stress reductor. It also has an anti fungal/bacterial function, and some research suggests that it plays a vital role in fighting cancer cells.
It’s also heavily used in the cosmetics industry.
OTHER STORIES YOU MAY ENJOY...
WHAT IS LIMONENE? READ THIS...