How Cannabis Promotes Homeostasis
How Cannabis Helps Maintain Body Homeostasis from CannabisNet on Vimeo.
The human body is biologically designed to look for balance. This state of equilibrium that the body seeks to achieve is called homeostasis.
Think of homeostasis as an internal “check and balance” system of the body that helps you function optimally. The trillions of cells within our body work independently and with each other to ensure we are alive and healthy. And because the human body is a single unit, when there is any change in the body’s systems it will affect one or more of the others.
Homeostatic Processes
A group of nerve cells, known as the hypothalamus, are found deep within our brains. The hypothalamus is essential in regulating key processes that we do everyday, that we never even notice them yet they are critical to maintaining homeostasis.
These include:
Sleep: Homeostasis is dependent on a healthy sleep-wake cycle, which is defined as the amount of time that has passed since the last time you got enough sleep. Sleep deficits result in a compensatory increase in the duration and intensity of sleep, while too much sleep will decrease sleep propensity.
Blood pressure: Blood pressure is regulated when cells in the body send feedback to the brain. Cells send signals that widen the blood vessels to eliminate pressure or narrow the vessels to increase pressure.
Breathing: Respiration rate is affected by how much carbon dioxide you have in your blood, which is controlled and monitored by a part of your brain. This process changes as you engage in certain activities, such as when you breathe deeper and more when you climb up a set of stairs because your muscles are burning more oxygen.
Mood: Our moods change based on changes, triggers, and stressors in the environment.
The hypothalamus is the primary command post, which is responsible for identifying changes in the environment and acting in response to it by releasing hormones as well as neurotransmitters, which then allow cells and structures in the body to communicate. For example, when you exercise, you become red. This is the result of your blood vessels dilating to reduce the increase in body temperature, as well as the increase in heart rate and breathing to make sure that oxygen levels in your body are adequate. These things happen as a response to your body seeking balance after exposed to a stimulus – exercise.
Disruption of Homeostasis
When homeostasis is interrupted because of illness, disease, injuries, or medications, the body cannot achieve that balance.
Many of the most common illnesses that plague the world today are caused by disrupted homeostasis. These include diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, arthritis, osteoporosis, gout, endocrine disorders, and thyroid disorders. Is it a surprise that these conditions are also treated by cannabis?
Age also affects homeostasis. Things within our body just don’t function as well, and the bones aren’t the only parts that get rickety over time. Even our cells don’t work as well when we get older. Many age-related conditions have its root in a lack of homeostasis, including arthritis and osteoporosis. On the other hand, conditions like chronic pain give us homeostatic symptoms due to the disruption of the cannabinoid cycle. Patients suffering from chronic pain may also suffer from depression, sleep problems, blood pressure, and heart rate issues. These symptoms occur because the endocannabinoid system (ECS) has to work overtime because of the constant pain.
How Cannabinoids Restore Homeostasis
Studies show that when we consume cannabinoids from cannabis, it can help restore or maintain homeostasis especially as we age. In fact, the MAIN JOB of the endocannabinoid system is to promote homeostasis.
How exactly?
The ECS has three main components:
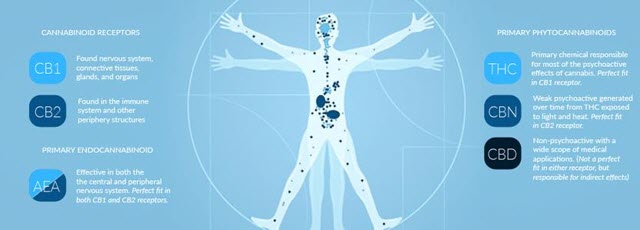
Cannabinoid receptors: These receptors are located on the surface of cells and monitor for conditions that occur outside the cell. They are responsible for transmitting information to the inside of the cell, because any change in conditions will then trigger the necessary cellular responses. The two primary cannabinoid receptors are CB1 and CB2; CB1 receptors interact with the THC in cannabis which results in the “high” feeling. CB2 receptors are mostly concentrated in areas beyond the nervous system such as the immune system. But both receptors are found throughout your body.
Endocannabinoids: Endocannabinoids are the molecules that bind to and stimulate the cannabinoid receptors. But unlike THC and CBD, endocannabinoids are naturally produced by cells within the body. The two main endocannabinoids are 2-AG and anandamide, which are produced from molecules similar to fat, and they are located within the membranes. They are produced by the body when needed, which means that they are only synthesized and utilized when the body needs them instead of being stored away for future use, just like other molecules within the body.
Metabolic enzymes: The third part of the trifecta is the metabolic enzymes which obliterate endocannabinoids when they have been used up. FAAH and MAGL are the two main metabolic enzymes. FAAH metabolizes anandamide while MAGL metabolizes 2-AG. These two make sure that the endocannabinoids are used when they are needed but not for longer than that.
These three components are located in almost every major system in the human body. When something results in a disruption of homeostasis, these three things work together to restore homeostasis.
According to Dr. Vicenzo Di Marzo, the Research Director at the Institute of Biomlecular Chemistry in Italy: “With the ‘pro-homeostatic action of the ECS’ we mean that this system of chemical signals gets temporarily activated following deviations from cellular homeostasis. When such deviations are non-physiological, the temporarily activated ECS attempts, in a space- and time-selective manner, to restore the previous physiological situation (homeostasis).”
A report published in Endocrine, Metabolic, and Immune Disorders – Drug Targets, says that: “The ECS (endocannabinoid system) has deep phylogenetic roots and regulates many aspects of embryological development and homeostasis, including neuroprotection and neural plasticity, immunity and inflammation, apoptosis and carcinogenesis, pain and emotional memory, and the focus of this review: hunger, feeding, and metabolism.”
Dr. Dustin Sulak, an osteopathic doctor and a Diplomat of the American Academy of Cannabinoid Medicine, says that our endocannabinoid system is “perhaps the most important physiologic system involved in establishing and maintaining human health.”
Additionally, by facilitating communication between various cells, endocannabinoids help regulate homeostasis. “At the site of an injury, for example, cannabinoids can be found decreasing the release of activators and sensitizers from the injured tissue, stabilizing the nerve cell to prevent excessive firing, and calming nearby immune cells to prevent the release of pro-inflammatory substances”, writes Dr. Sulak.
Conclusion
Humans, as a functioning, single-unit organism, need a well-balanced internal system in order to grow and function optimally. An imbalanced state of homeostasis can lead to health problems ranging from minor headaches to more serious, life-threatening conditions including cancer. The endocannabinoid system helps regulate important processes that maintain homeostasis by activating cannabinoid receptors in the central nervous and peripheral nervous systems.
You too, can restore homeostasis by eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, exercising, and consuming cannabis in a form that suits you best.
How Marijuana Promotes Homeostasis from CannabisNet on Vimeo.
OTHER STORIES YOU MAY ENJOY...
THE MARIJUANA BODY MAKEOVER, READ THIS...